The solar panels that you typically see on a roof in the UK are called Photovoltaic Solar Panels. Photo stands for light and voltaic is associated with electricity. Photovoltaic is often referred to as “PV” and as the name suggests, the solar panels convert light directly into electrical energy. You maybe thinking how do they work and exactly how much sunlight do they need to operate efficiently? Of course most importantly, is it sunny enough for the often cloudy conditions of the United Kingdom?
Photoelectric Effect
The solar PV panels produce electricity by way of a process called photoelectric effect, which was first quoted in 1839 by a French physicist named Edmund Bequerel. He highlighted how certain materials produce an electric current when they are exposed to light and it is this same principle that is in operation with solar PV panels.
The first uses for solar PV panels were on space craft way back in 1960’s and since then the technology has significantly improved with the solar panels becoming smaller and more efficient. Following years of progression solar PV panels are now an affordable and efficient renewable technology for domestic and commercial properties.

Solar Cells, Panels & Arrays
Solar cells are the devices which convert sunlight into electricity. A single cell on its own is not sufficient to provide electricity for a property and only delivers a very small amount of power. Then there are several cells connected and grouped together in a frame to construct a solar PV panel. This is also referred to as a PV module. With the cells combined into a panel, a larger, more useful amount of power can be generated. When you see several panels connected together on a roof or ground location, this is known as a solar array. See more information on solar technology and compare solar panels.
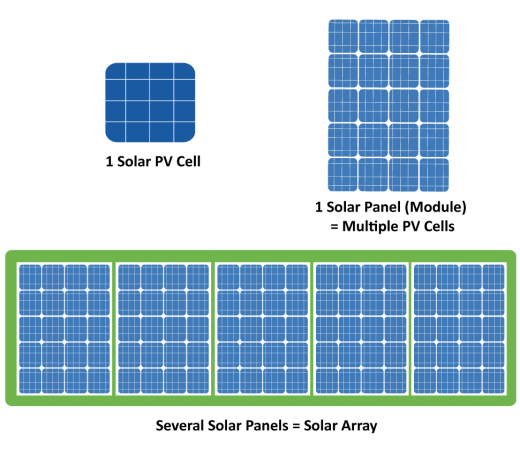

How Are Solar Panels Constructed?
Within the solar cell itself, you will find two wafer-thin layers of silicon crystal, that are placed on top of each other to construct a silicon like sandwich. The top layer of silicon crystal has been specially treated with atoms that are unstable, so that electrons can be released. The bottom layer has also been treated, however the atoms have a few empty spaces so that other electrons can fill the space.
The top layer of silicon crystal wants to a lose some electrons, while the bottom layer wants some more electrons. The electrons actively want to move from the top layer to the bottom. With this structure in place, it enables electricity to be produced, however the electrons within the silicon crystal are not able to move freely until the solar panel is exposed to light.
When sunlight hits the solar panel, it energises the electrons and gives them enough energy to move. As such, the electrons flow from the top layer of silicon crystal to the bottom. As the electrons move in the same direction, electricity is produced. With two metal contacts placed on either side of the silicon sandwich, you will then have electricity moving through a circuit.
Converting The Current
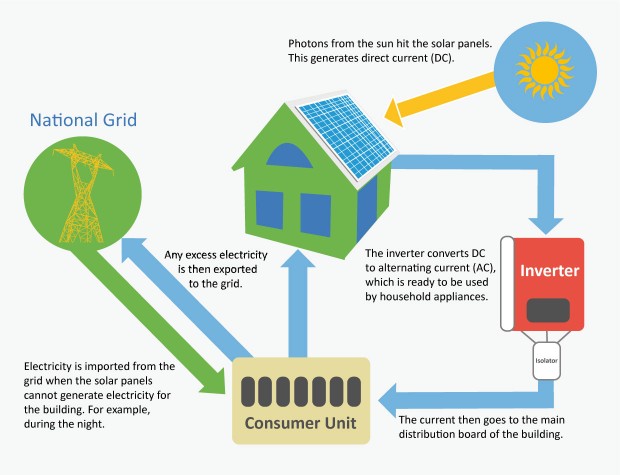
Light hits the solar PV cells, generating direct-current electricity (DC) but the electricity used in a property is alternating-current (AC). As such, the electricity needs to be converted using an inverter, which is typically installed in a loft. With the electricity converted to alternating-current it can then be fed into the property to operate appliances. See the diagram below, which also highlights how electricity is imported from the grid when the panels are not generating electricity during non-daylight hours.
Do They Work In The UK?
Solar PV panels are able to harness clean energy from what you may classify as a virtually limitless supply. This sounds fantastic if you live in Australia but what happens if you live in the UK where there is not enough sunshine for solar panels? Well, despite our unpredictable weather, the sun doesn’t need to be out for solar panels to work.
As you would assume, solar panels do work well on a sunny day, but they do produce a significant proportion of energy on a cloudy day. It is not about the temperature, the more light available, the more electricity they produce.
Crucially, solar panels utilise light to produce electricity and not heat. In fact, too much heat on a long, hot sunny day can be detrimental to the efficiency of the solar panels. As such, a moderate, long summer day in the UK is likely to deliver a significant output from a solar PV system.
Renewable Technology Usage In Europe
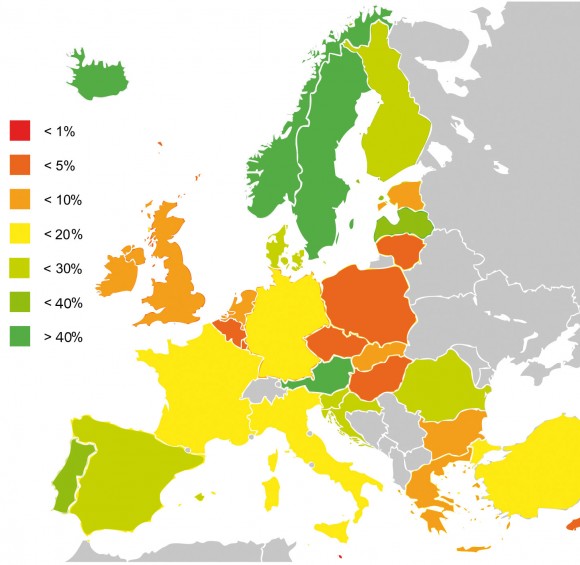
Not Africa But…
Although Britain is not in the same league as Spain or Africa, many parts of the UK receive a similar amount of sunlight to Germany, which is currently one of the leading solar power countries. There is significant growth in the UK and by 2020 it is expected 10 million homes will have solar PV.
The government have also introduced the feed in tariff to encourage the take-up of solar PV to help both families and businesses to make a very reasonable return on their investment, while making a contribution to reducing carbon emissions.


